Journalists have less trust in social media due to the spread of fake news.
The credibility of social media sites for journalists has dropped significantly over the past four years - according to the latest survey conducted by Trendlabor Mediaindex. The main reason for the loss of trust is the increased spread of fake news, with which almost everyone regularly meets. This did not decrease the use of social media in journalism: the proportion of those who regularly use these interfaces to collect information has increased close to 90%, but four fifths of them pay more attention than before to filter out false information.
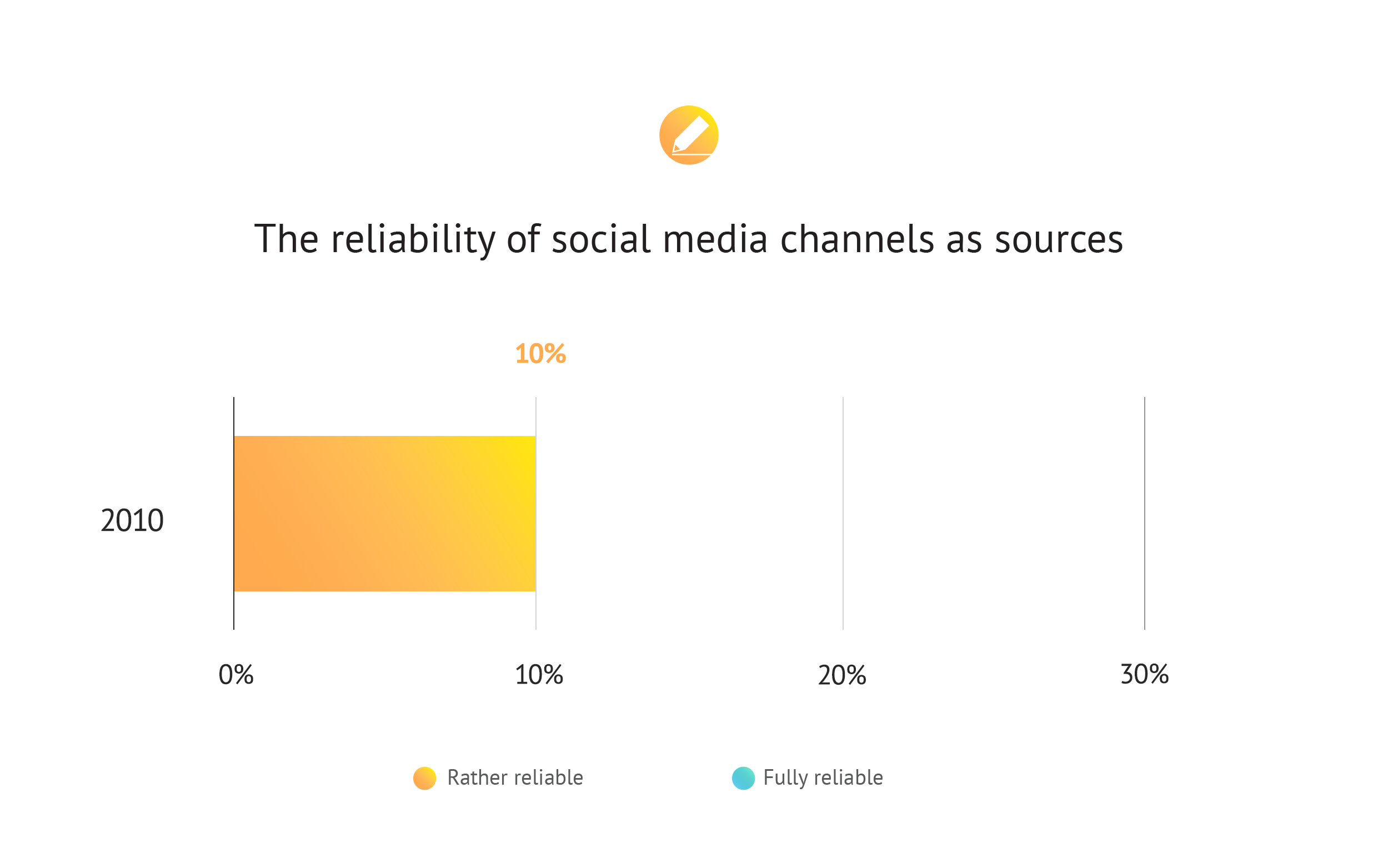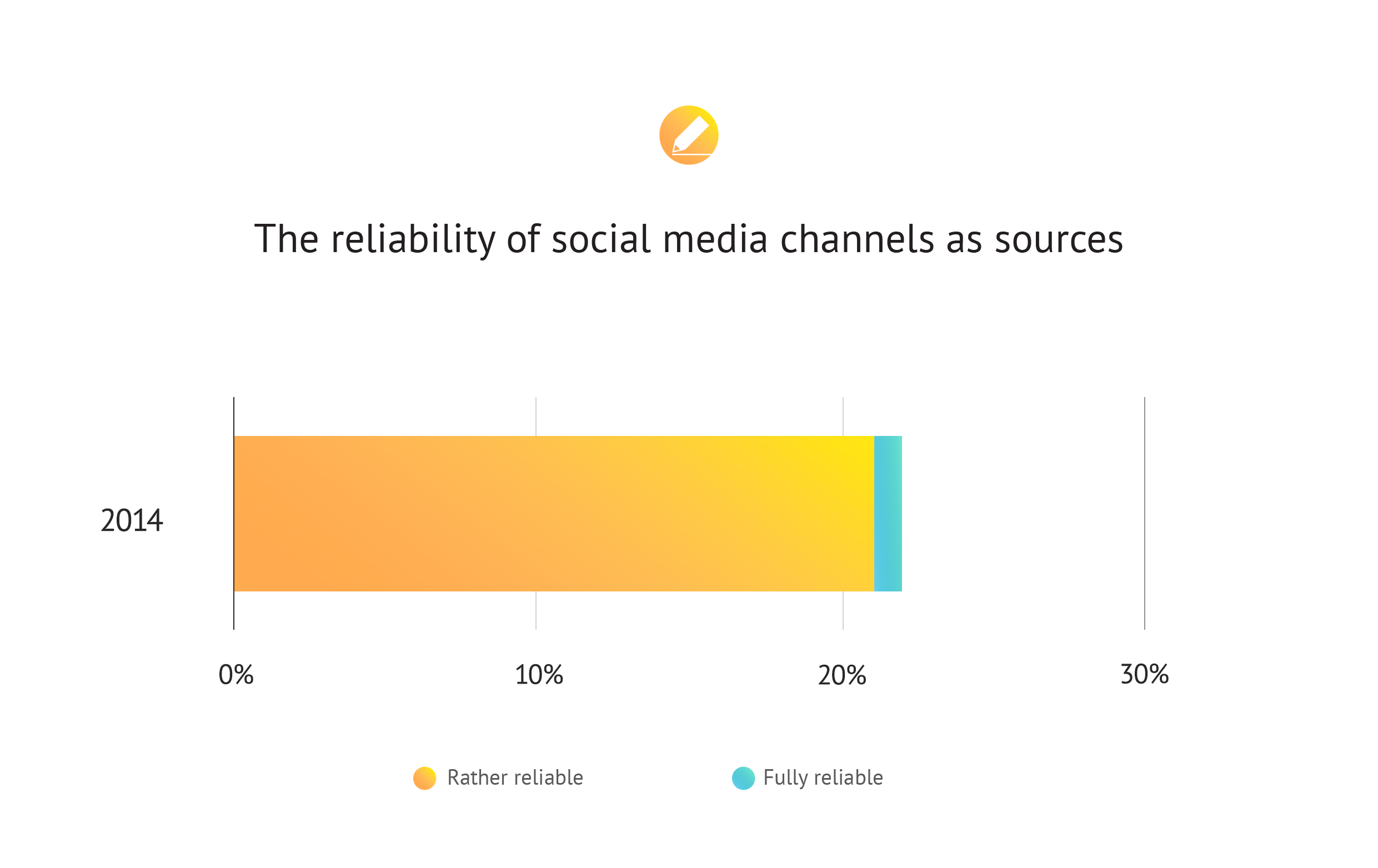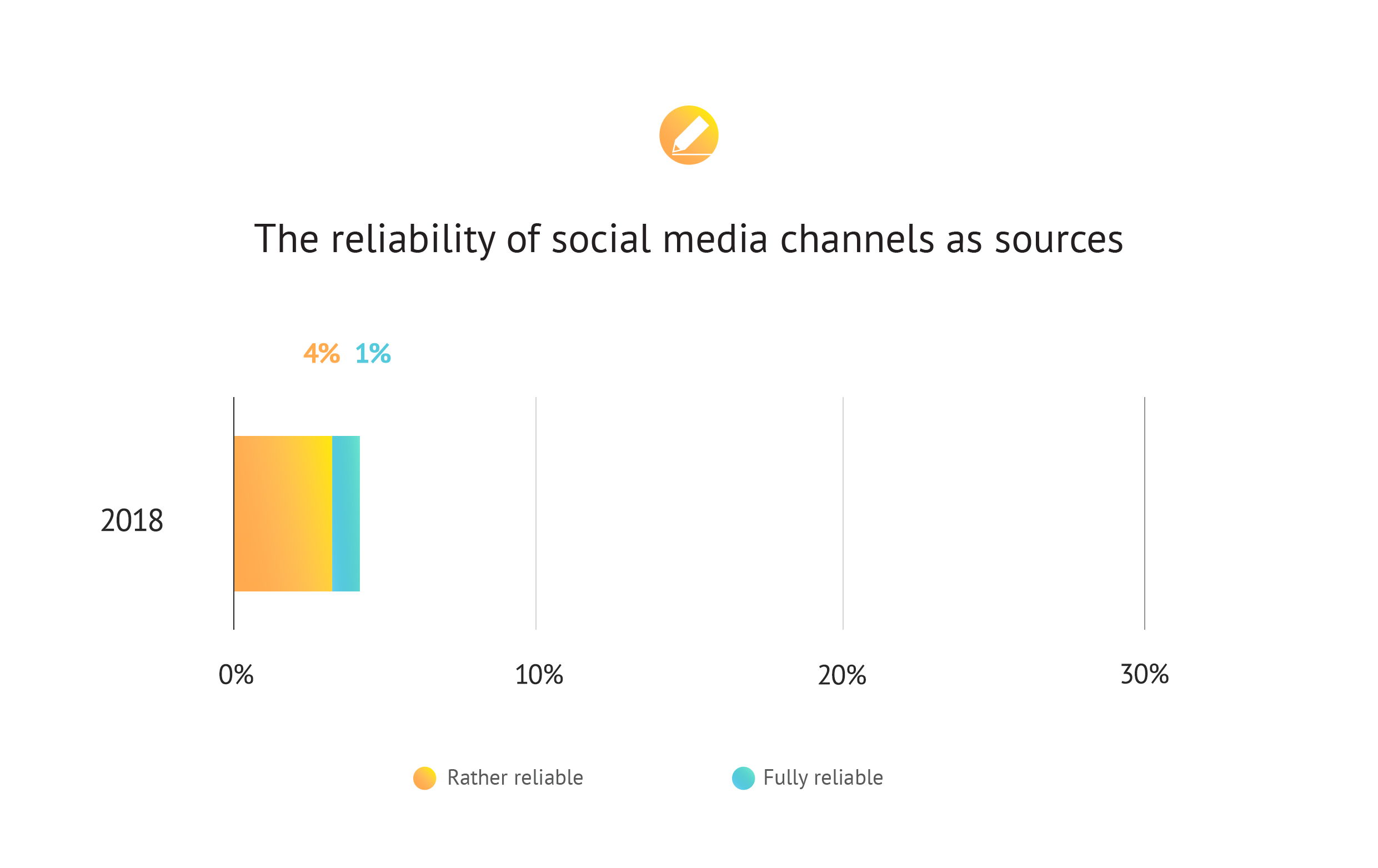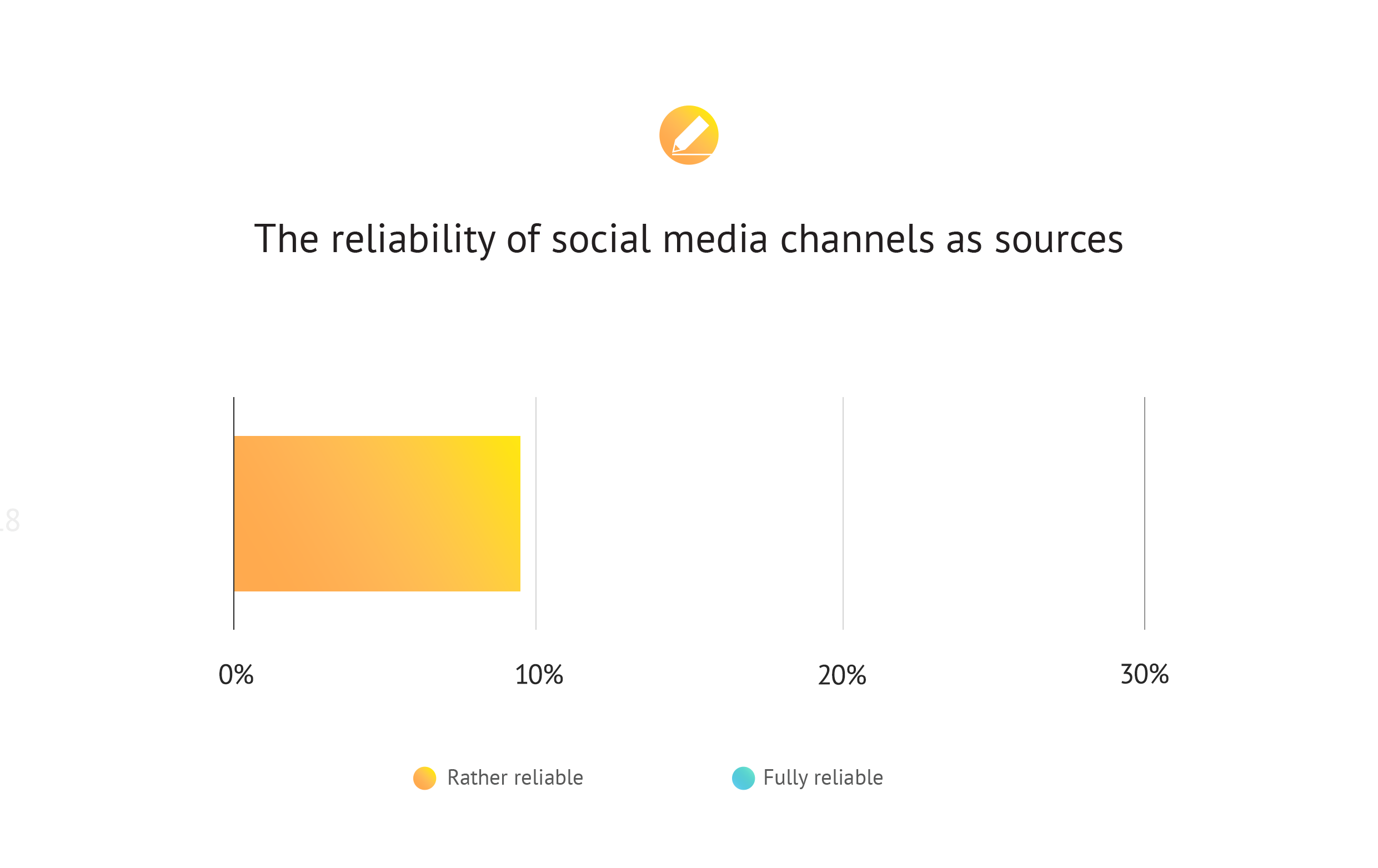
For the third time, a survey was conducted by FLOW PR among journalists about the use of social media sites. Comparing the results of the Trendlabor Mediaindex survey, which has been carried out every four year since 2010, it can be concluded that trust in social channels has dropped significantly in the past four years: the number of those who believe that these interfaces cannot be considered as reliable sources has doubled. The proportion of journalists who consider the mentioned platforms rather reliable than not and would use them to collect information for their work has dropped to 4% from the previously measured 21%.
The change is related to the spread of fake news, with wich 94% of journalist at least weekly, but more than 50% of them daily come across when browsing social platforms. One third of the respondents partly, and half of them fully agree that as a result social sites are less likely to be credible sources than before. According to three quarters of journalists, these platforms play an important role in the formation and spread of fake news, with only 28% agreeing partly or completely that the most popular social sites have taken effective steps to stop disinformation.

In line with the new situation, more than four-fifths of press staff pay more attention than used to in order to filter out fake news. At the same time, nearly 70% of respondents say that the greater competition in providing news in some aspects results in difficulties in checking the sources of the news available on the internet. This is also evidenced by the fact that one fifth of the respondents fully, and 42% of the respondents partly believe that the spread of fake news in social media has led to the appearance of more fake news in traditional media as well.
“The trust of journalists in the credibility of social media has apparently dropped. The increased spread of fake news has created a new situation in recent years resulting in that journalists have become more critical when using social media platforms and are even more concerned with controlling the sources,” emphasised the results of the survey Botond Sajti, Managing Partner of FLOW PR.
Majority of journalists are on the same page that the ever-increasing number of fake news cannot be by accident but is a conscious human activity. According to almost 90% of the respondents the spread of fake news is also helped by the lack of information of the internet users.
About Trendlabor Mediaindex survey
The aim of the survey conducted by FLOW PR for the third time is to investigate how journalists use social media in their work and in their leisure time. The first survey was conducted in 2010 and the second one in 2014. The survey was conducted between the 2nd and 29th of October 2018 using an online questionnaire. Nearly 200 journalists contributed to the survey coming from public, economic, tabloid and lifestyle media, as well as from thematic media (real estate, health care, IT, etc.).
